|
|
synonyms: metacarpal fracture, metacarpal shaft fracture
Metacarpal Shaft Fracture ICD-10
Metacarpal Shaft Fracture ICD-9
- 815.03(closed)
- 815.13(open)
Metacarpal Shaft Fracture Etiology / Epidemiology / Natural History
- Angulation >30 degrees or shortening >4mm can lead to grip weakness, loss of endurance, cramping and clawing.
- Any rotational deformity can lead to digital overlap during finger flexion
Metacarpal Shaft Fracture Anatomy
- Metacarpals are concave on the palmar surface, thus plates should be pre-bent to avoid volar gaping at the fracture site.
- 2nd and 3rd metacarpals articulate with the trapezoid and capitate. Limited motion exists in 2nd, 3rd CMC joints.
- 4th and 5th metacarpals articulate with the hamate and have greater
- Intermetacarpal ligament prevent more than 3-4mm of shortening. (Eglseder WA, JOT 1997:11:441)
- 7degree extensor lag develops for every 2mm of metacarpal shortening. (Strauch RJ, J Hand Surg 1998;23Am:519)
- See Hand Anatomy.
Metacarpal Shaft Fracture Clinical Evaluation
- Generally have obvious pain and deformity at the fracture site.
- Document neurovascular status of the finger before and after any reduction.
- Evaluate cascade, any scissoring or overlap indicates need for reduction +/- fixation
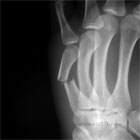
Metacarpal Shaft Fracture Xray
- P/A and lateral views of hand
- 30-45 degree suppinated or pronated views
Metacarpal Shaft Fracture Classification / Treatment
- Non-displaced
-buddy taping (CPT=26600 closed treatment MC fracture without manipulation, each bone: 26605=with manipulation)
- Displaced (angulation >30 degrees, shortening >4mm, any rotational deformity) (every 2 mm of metacarpal shortening results in 7 degrees of extensor lag. (Strauch RJ, J Hand Surg Am. 1998 May;23(3):519-23).
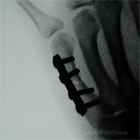
-CRPP vs ORIF
-Long oblique fractures may be treated with parallel miniture screw fixation (Freeland, Orthopaedics 17:199;1994).
-Tranverse fractures may be treated with intrameduallary nails (Gonzalez MH, CORR 1996;327:47) or ORIF with mini-plates. (Bosscha K, Injury, 1993;24:166)
- Open fracture: consider mini-external fixation. (Freeeland AE, CORR, 1987;214:93)
Metacarpal Shaft Fracture Associated Injury
Metacarpal Shaft Fracture ORIF Complications
Metacarpal Shaft Fracture Follow-up
- Post-op: Splint in "safe" position (wrist extended 15-20 degrees, MCP joints flexed 70 degrees, PIP joint in 0-10 degrees flexion)
- 7-10 Days: remove splint. Place in removable splint with fingers buddy-taped. Encourage gentle ROM
- 6 Weeks: Check xrays. Progress with ROM exercises. Activity modifications: no heavy manual labor, no contact sports, no lifting >5 lbs.
- 3 Months: Check xrays. If union is complete return to full activities. Assess motion, consider occupational therapy if indicated.
- 6 Months: Assess motion,
- 1Yr: F/u xrays, assess outcome.
Metacarpal Shaft Fracture Review References
- Rockwood and Greens
- Greens Hand Surgery
- Freeland AE, Geissler WB, Weiss AP, Operative Treatment of Common Displaced and Unstable Fractures of the Hand, JBJS 2001;83A:928-945
- Henry MH. Fractures of the proximal phalanx and metacarpals in the hand: preferred methods of stabilization. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2008 Oct;16(10):586-95
- Freeland AE, Orbay JL. ORIF of the Tubular Bones of the Hand In: Stickland JW, Grahma TJ, editor. Hand 2nd ed. Master Techniques in orthopedic surgery. Philadeplhia: Lippincott-Raven; 2004. p 3
|